Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
What is Intelligence?
Intelligence has been defined in many different ways including as one's capacity for logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, planning, creativity and problem solving. It can be more generally described as the ability to perceive information, and retain it as knowledge to be applied towards adaptive behaviors within an environment or context.
Artificial Intelligence vs. Computational Intelligence
Artificial
Artificial Intelligence refers to systems that simulate intelligence. The focus is to create systems that give the appearance of human-like intelligence
Focused on the result no matter what method is used to achieve it.
Computational
Computational Intelligence focuses on creating systems that "think" in the same way that humans think.
Focused on the way the machine will process information.
The purpose of AI is to get computers to show characteristics of Human intelligence which may include:
learning, problem solving, creativity, understanding, planning, logic.
Planning

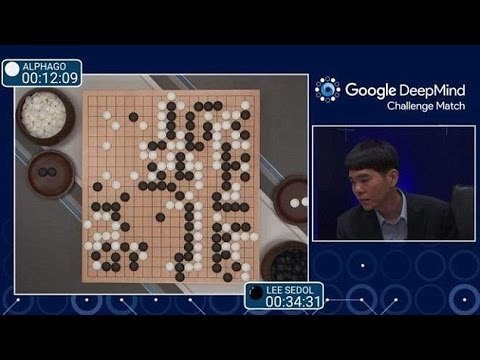

http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-the-computer-beat-the-go-master/
creativity

http://deepdreamgenerator.com/

Understanding

Learning
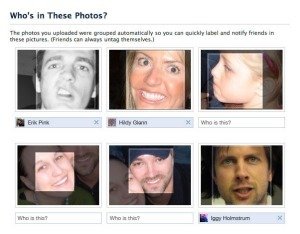
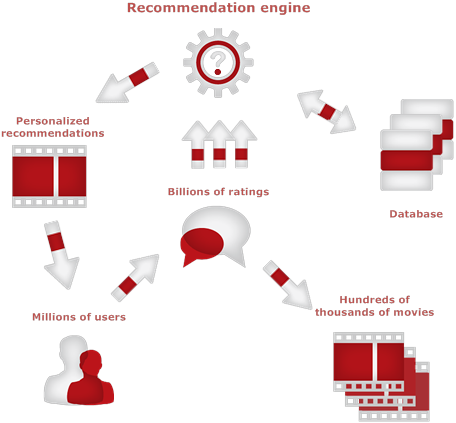
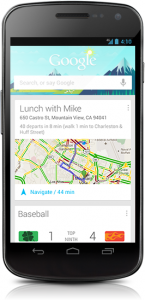
Problem Solving
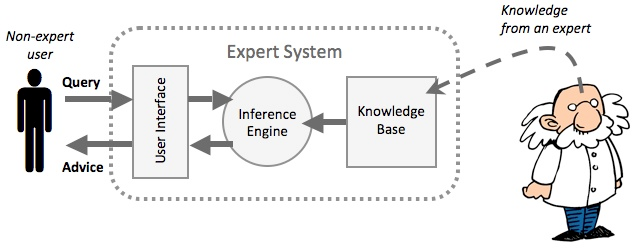
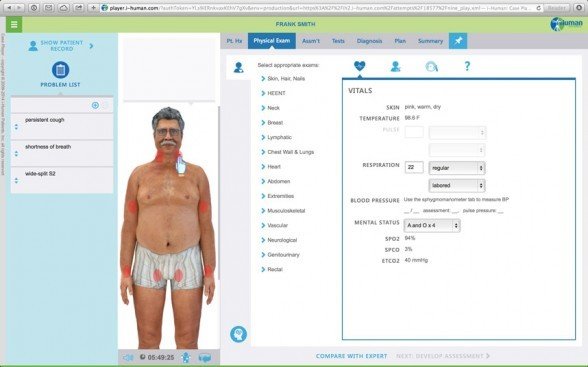
Expert System
An Artificial Intelligence applied to a specific knowledge domain. Can do one thing very well.
Relatively simple tasks.
Components
- User Interface
- Inference Engine (AI engine)
- Decision trees
- Inference Rules
- Fuzzy Logic
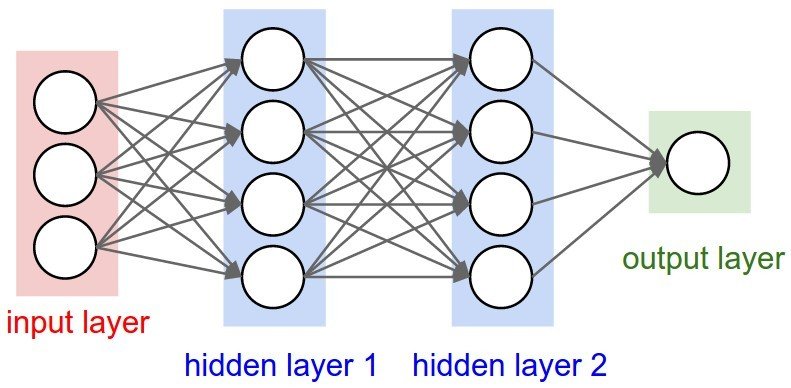
- Neural Network
- Knowledge base

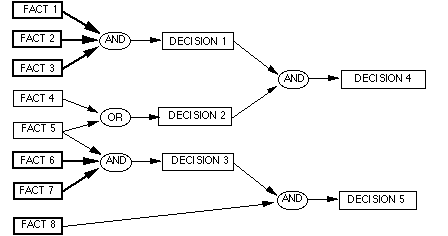

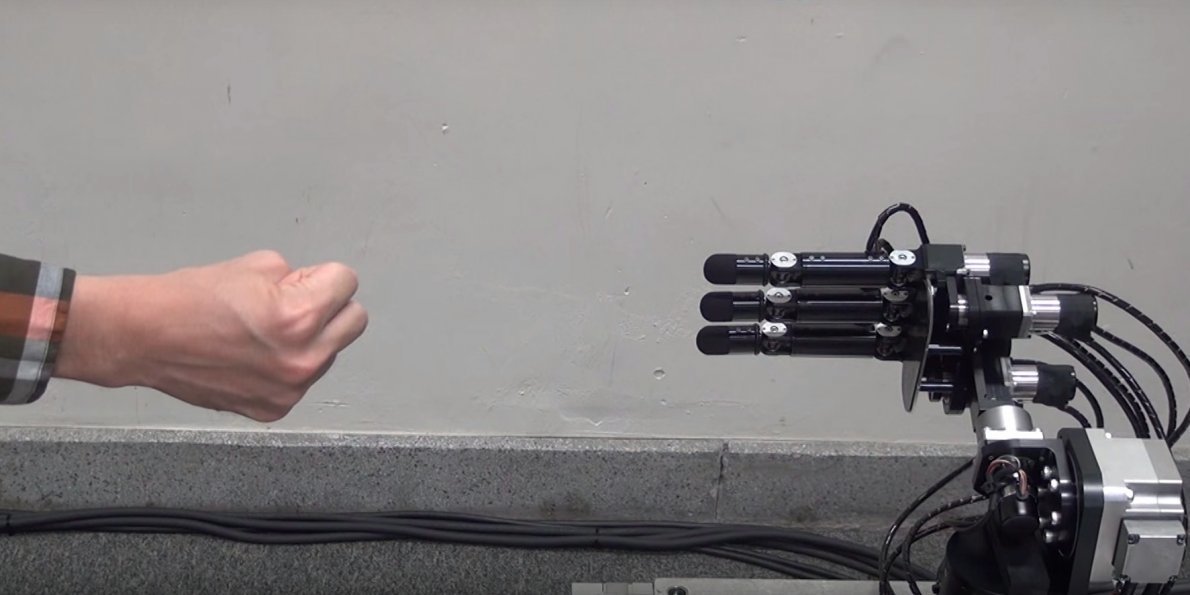
This AI plays Rock Paper Scissors.
TASK: Create a decision tree for this robot.
Limitations
- Complexity of the Inference engine
- Exceptions to the rule
- Integrity of knowledge base
Learning Computers modify their knowledge base and their inference engine based on experience.
Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
By Victor Castro
Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
- 1,123



