Static Analysis
Static Analysis
2 .What do we want to know about a binary?
3. What else can we learn about a binary before talking about code?

1. Why Static analysis?
We want to learn as much as we can about the binary without having to run it.
This way we can save ourselves from running a malicious program, or even save time just from getting hints for other analysis!
That depends on what we are doing! But generally starting with Readelf/Strings is helpful
Static tools demo
- readelf
- strings
- objdump
- xxd
What is a basic block?
Basic block is a set of instructions where the only entry is the top of the block and the only exit is the end of the block.
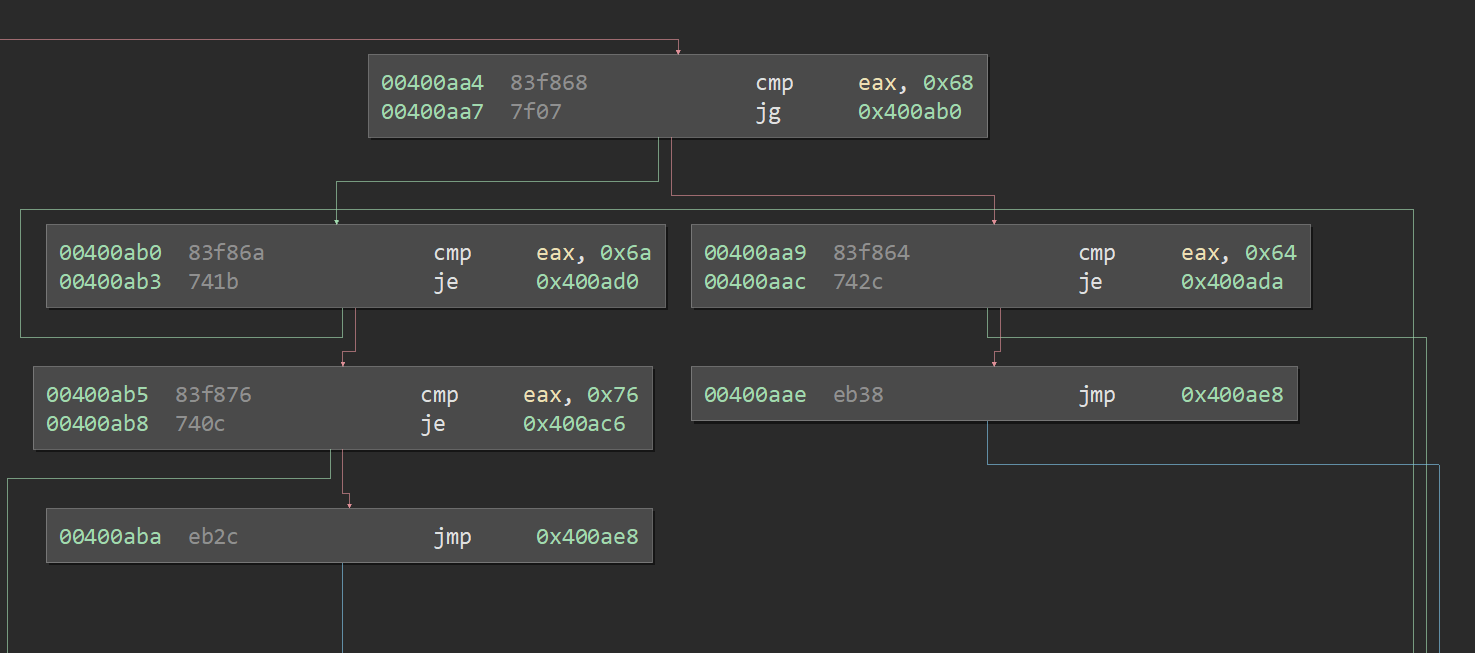
In Binaryninja, red is false path,
green is true path,
blue is neither (sometimes greeen).
What is a basic block?

Address Opcode Instruction Operand(s)
May need change options for seeing address and opcodes in your disassembler!
Basic blocks are part of Intraprocedural scope, which means within a single function
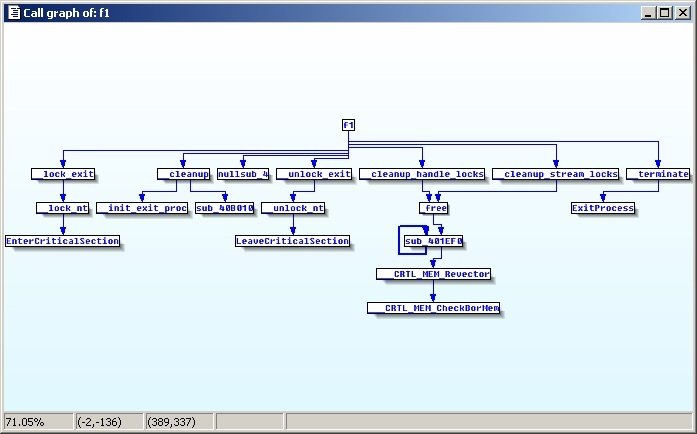
Call Graphs
IDA can show you call graphs visually. Can be useful and depending on the type analysis is needed (interprocedural).
Binary Ninja
We can use binja to disassemble and it is the best looking one!
Has many plugins, built on python, the Sublime of disassembly
Binary Ninja
IDA
IDA is the oldest, works well on windows binaries, detects structures, colors are customizable (if you're into that)
Little harder to use, but you get more analysis tools in the background. Basically operates the same way you would Binja
Emacs of disassembly
IDA
Radare2
Originally written as a hexeditor, grew into a massive disassembler
/debugger/forensics tool all at the same time.
Really hard to use, super powerful, can do pretty much anything. CLI, no good GUI
Vim of disassembly plus a toaster&blender&knife set.

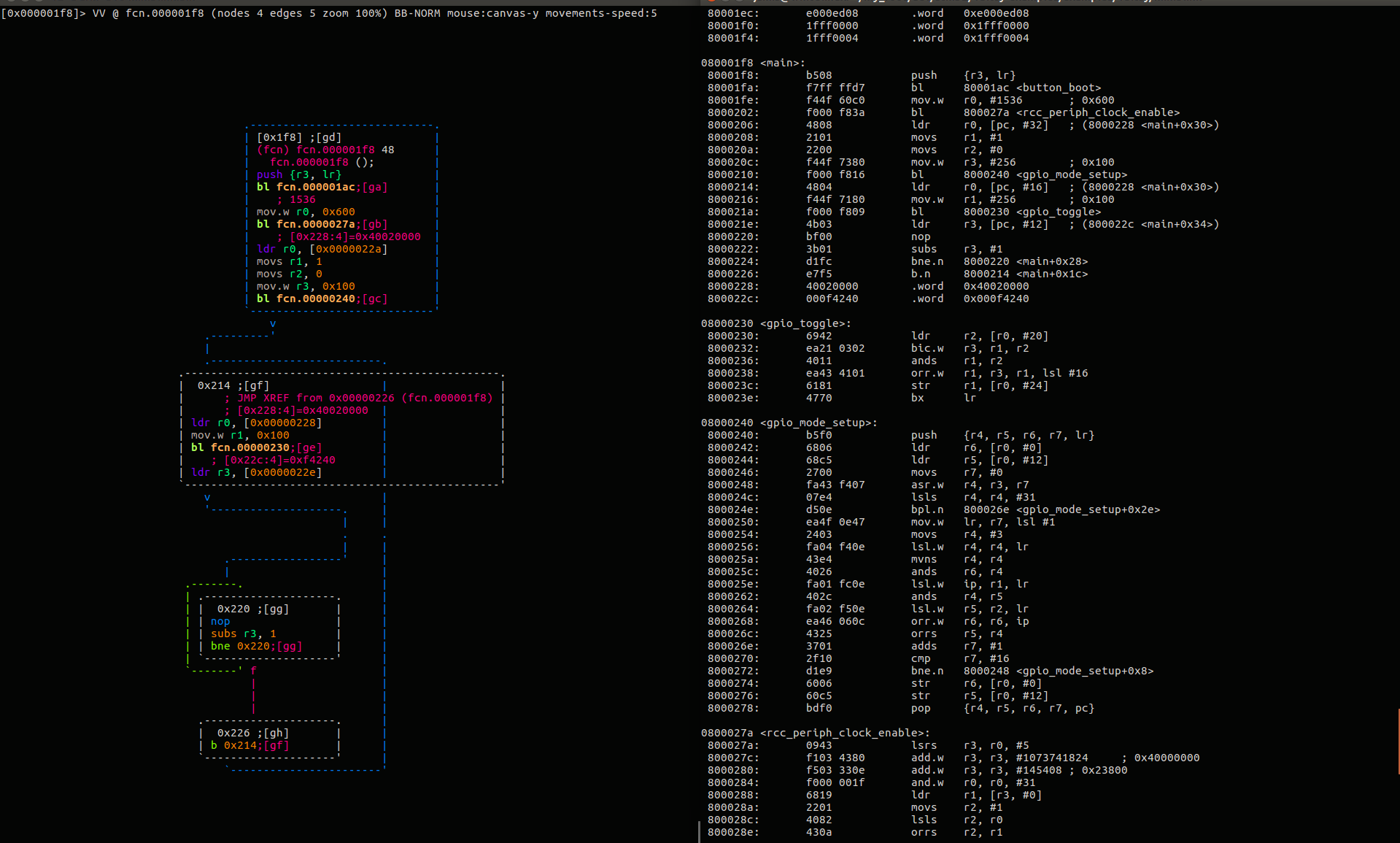
Radare2
Ghidra
Open source Disassembler recently released by the NSA.
Decompilation feature that would cost a lot of money otherwise

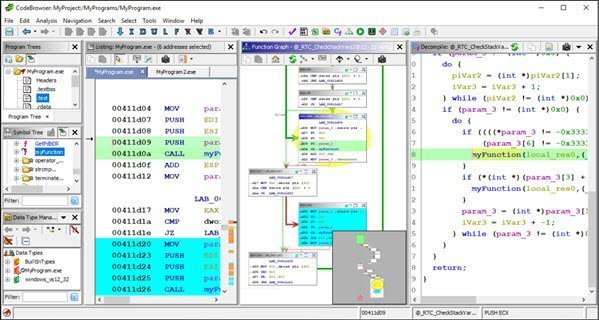
Ghidra
Function Detection
How might we detect functions in a binary? Assuming the binary is stripped
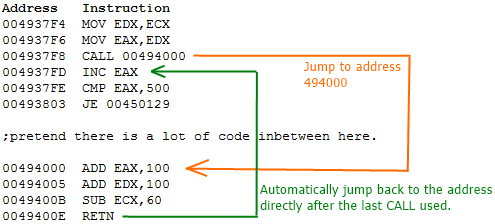
Function Detection
Recursively, we can try to detect all the functions by disassembling at a call instruction address

Can this be defeated?
Function Detection
Linearly, we can look for function initialization code, such as the snipped below.
Can this be defeated?
foo:
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
...
do stuff
...
pop ebp
retInitialize the stack frame (start of function)
remove stack frame (end of function)
Control Flow Analysis
What are the possible control flow structures?
+ For, While, Do While loops
+ If, If-else statements
+ Switch statements
In Assembly, do these look different?
+ in assembly they do not
look very different at all
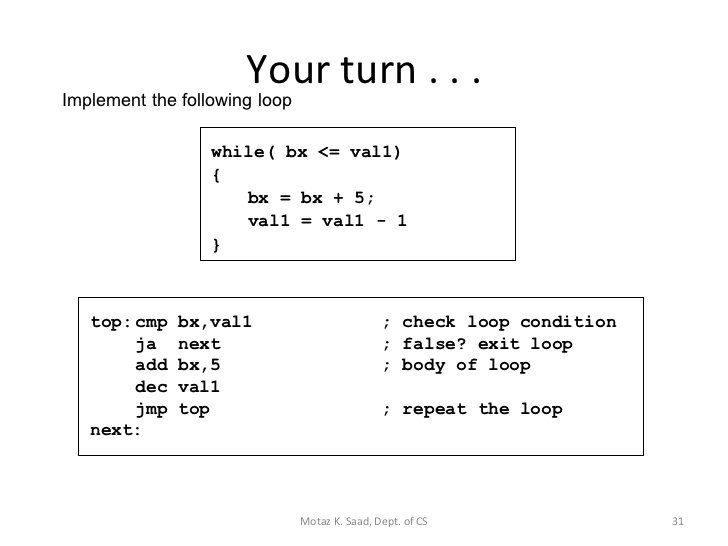
Control Flow Analysis
If all loops look the same, why should we care if they are different?
Well we don't care actually.
How might we detect a loop then?
Perform DFS
1: top
2: top, next
3: top,
4: top, top *loop found*

Data-Flow Analysis
Data-flow analysis is a technique for gathering information about the possible set of values calculated at various points in a computer program
-wikipedia
+ Forward/Backward Analysis
+ Flow/Path/Context Sensitive
+ May/Must join points
There is a lot to talk about here, but too much for our class! For more check these 430 slides out!
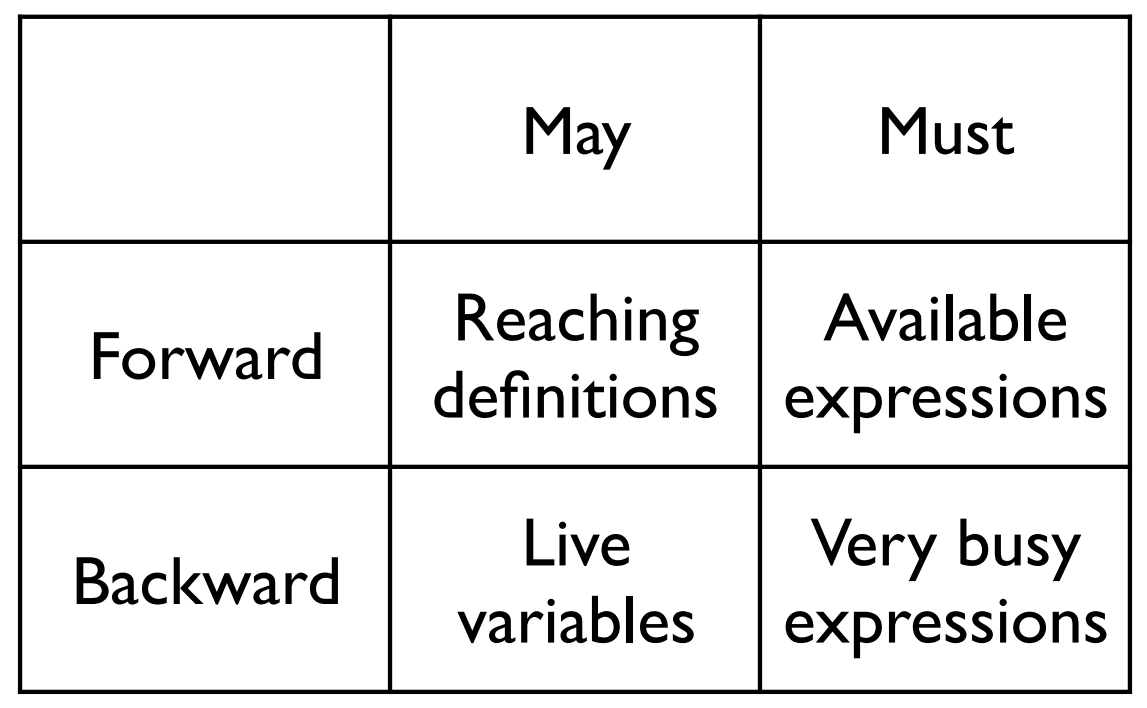
Data-Flow Analysis

after slicing
Program slicing is a great example of an analysis that would be useful to a Reverse Engineer!
This shows us on what affects sum prior to the chosen line (write(sum)).
(Backward analysis)
Notice lines with 'w' are still included since w affects the definition of sum in the for loop.
Program slicing is not exclusively backward like other data-flow analyses
Static Analysis Frameworks
Angr - python library for analysis and powerful for symbolic execution (later topic)
CIL - written in OCaml, for C, can do all the analysis mentions before on C source code.
LLVM - frame work for compiling and optimizing the LLVM IR, easily extended

Static Analysis
By Drake P
Static Analysis
- 371



