Week 3
Agenda
- Static Analysis, Deeper dive
- Library calls and System calls
Static Analysis
A Deeper Dive
Static Analysis
Readelf, objdump, file, strings, all great tools, but they aren't Analysis tools!
They help us analyze, but we want cool analysis done for us!
Disassemblers are only as good as you make them!
Function Detection
How might we detect functions in a binary? Assuming the binary is stripped
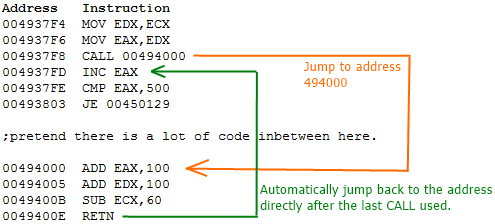
Function Detection
Recursively, we can try to detect all the functions by disassembling at a call instruction address

Can this be defeated?
Function Detection
Linearly, we can look for function initialization code, such as the snipped below.
Can this be defeated?
foo:
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
...
do stuff
...
pop ebp
retInitialize the stack frame (start of function)
remove stack frame (end of function)
Control Flow Analysis
What are the possible control flow structures?
In Assembly, do these look different?
Control Flow Analysis
What are the possible control flow structures?
+ For, While, Do While loops
+ If, If-else statements
+ Switch statements
In Assembly, do these look different?
+ in assembly they do not
look very different at all
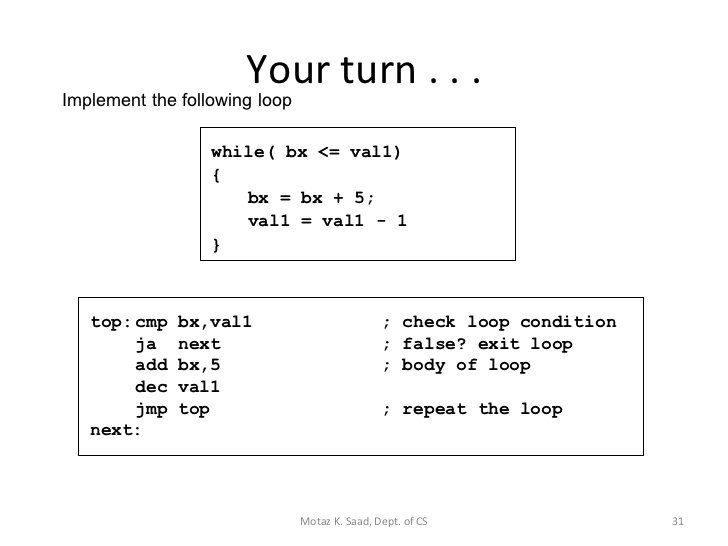
Control Flow Analysis
If all loops look the same, why should we care if they are different?
How might we detect a loop then?

Control Flow Analysis
If all loops look the same, why should we care if they are different?
Well we don't care actually.
How might we detect a loop then?
Perform DFS
1: top
2: top, next
3: top,
4: top, top *loop found*

Data-Flow Analysis
Data-flow analysis is a technique for gathering information about the possible set of values calculated at various points in a computer program
-wikipedia
+ Forward/Backward Analysis
+ Flow/Path/Context Sensitive
+ May/Must join points
There is a lot to talk about here, but too much for our class! For more check these 430 slides out!
Data-Flow Analysis

after slicing
Program slicing is a great example of an analysis that would be useful to a Reverse Engineer!
This shows us on what affects sum prior to the chosen line (write(sum)).
(Backward analysis)
Notice lines with 'w' are still included since w affects the definition of sum in the for loop.
Program slicing is not exclusively backward like other data-flow analyses
Static Analysis Frameworks
Angr - python library for analysis and powerful for symbolic execution (later topic)
CIL - written in OCaml, for C, can do all the analysis mentions before on C source code.
LLVM - frame work for compiling and optimizing the LLVM IR, easily extended

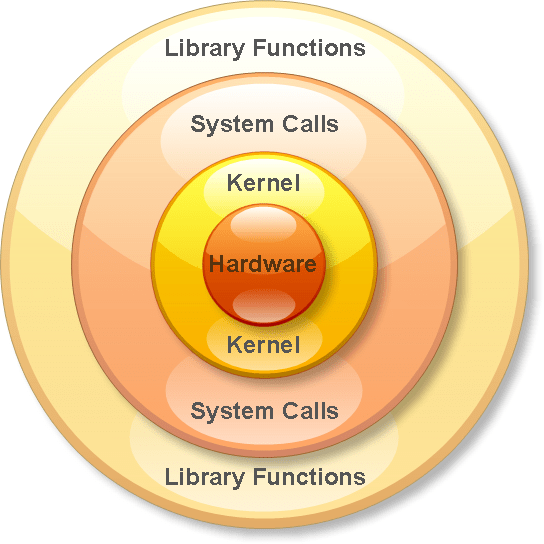
Library calls and System calls
Libc
The term "libc" is commonly used as a shorthand for the "standard C library", a library of standard functions that can be used by all C programs (and sometimes by programs in other languages).
-wikipedia
What is happening when we use printf in our binaries?
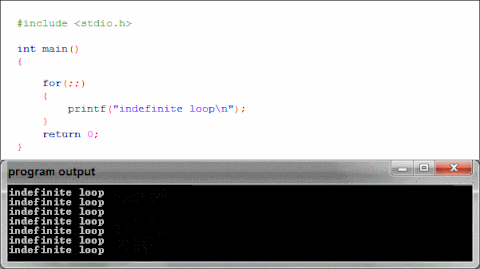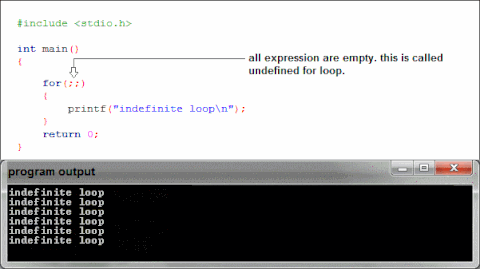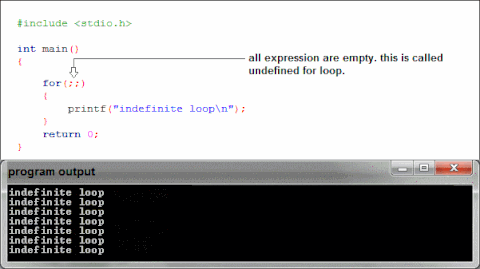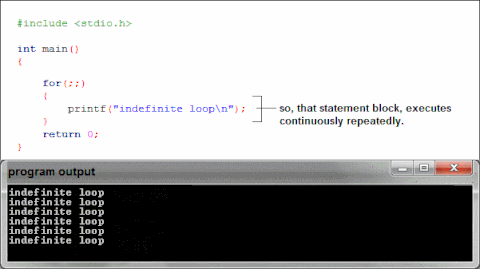
Libc
What is happening when we use printf in our binaries?
How does text make it to the screen?

printf gets linked to the first instance in the
included libraries of a printf, then printf does its
thing.
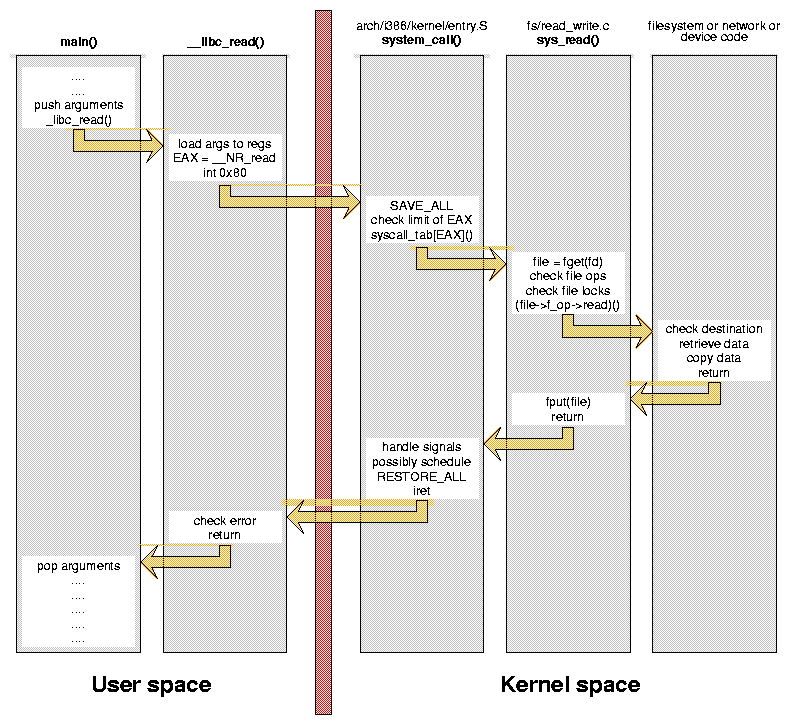
Libc to Systemcalls
How does text make it to the screen?

printf, malloc, read, write, etc. are all wrappers for
system calls.
System calls are the process' way of asking for
permission to do something with a resource.
System calls
Syscalls are not standardized on all architectures or Kernels
In Linux, they are interrupts ('int' 32bit or 'syscall' 64bit).
In Windows, depending on the version or architecture, you might see 'syscall' or 'int' or even just 'call'

System calls
What are these 'resources'?
Resources are anything the computer can do, reaching devices, printing to terminals, key presses, etc.
In windows, resources are called handles, and everything is an object. More wrappers for syscalls.
System calls
Simple in assembly:
; ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
; Writes "Hello, World" to the console using only system calls. Runs on 64-bit Linux only.
; To assemble and run:
;
; nasm -felf64 hello.asm && ld hello.o && ./a.out
; ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
global _start
section .text
_start: mov rax, 1 ; system call for write
mov rdi, 1 ; file handle 1 is stdout
mov rsi, message ; address of string to output
mov rdx, 13 ; number of bytes
syscall ; invoke operating system to do the write
mov rax, 60 ; system call for exit
xor rdi, rdi ; exit code 0
syscall ; invoke operating system to exit
section .data
message: db "Hello, World", 10 ; note the newline at the endLibrary calls
1. Linker sets up the Global Offset table in memory (.got)
2. When the function is called, we use an offset plus the .got address to call the correct function in the .plt (process linkage table).
3. From the linked function, we jump into the shared object to execute.
What does this all mean for attackers?

Week 3
By Drake P
Week 3
Static Analysis techniques and tools, Standard Libraries and GOT
- 365



