(Second-)largest component in
spatial random graphs
Joost Jorritsma
joint with Júlia Komjáthy, Dieter Mitsche
Papers: tiny.cc/cluster-size-ksrg



Cluster-size decay in supercrit. nearest-neighbor percolation




[Grimmett & Marstrand '90, Kesten & Zhang '90]
Cluster-size decay in supercrit. nearest-neighbor percolation


[Grimmett & Marstrand '90, Kesten & Zhang '90]
Cluster-size decay in Erdős–Rényi random graph



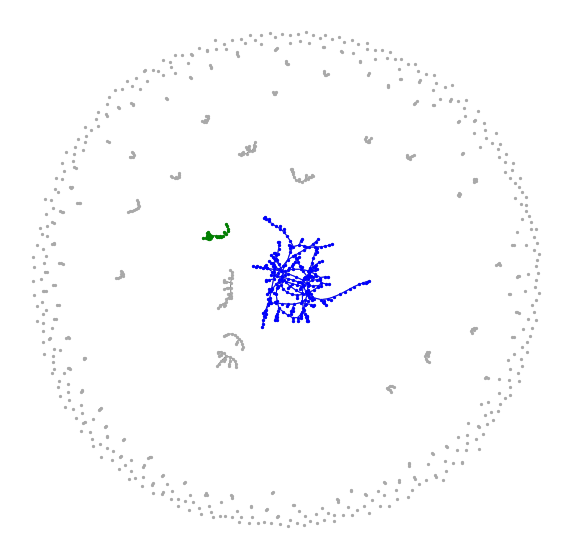





Hyperbolic random graph
Scale-free percolation
Long-range percolation
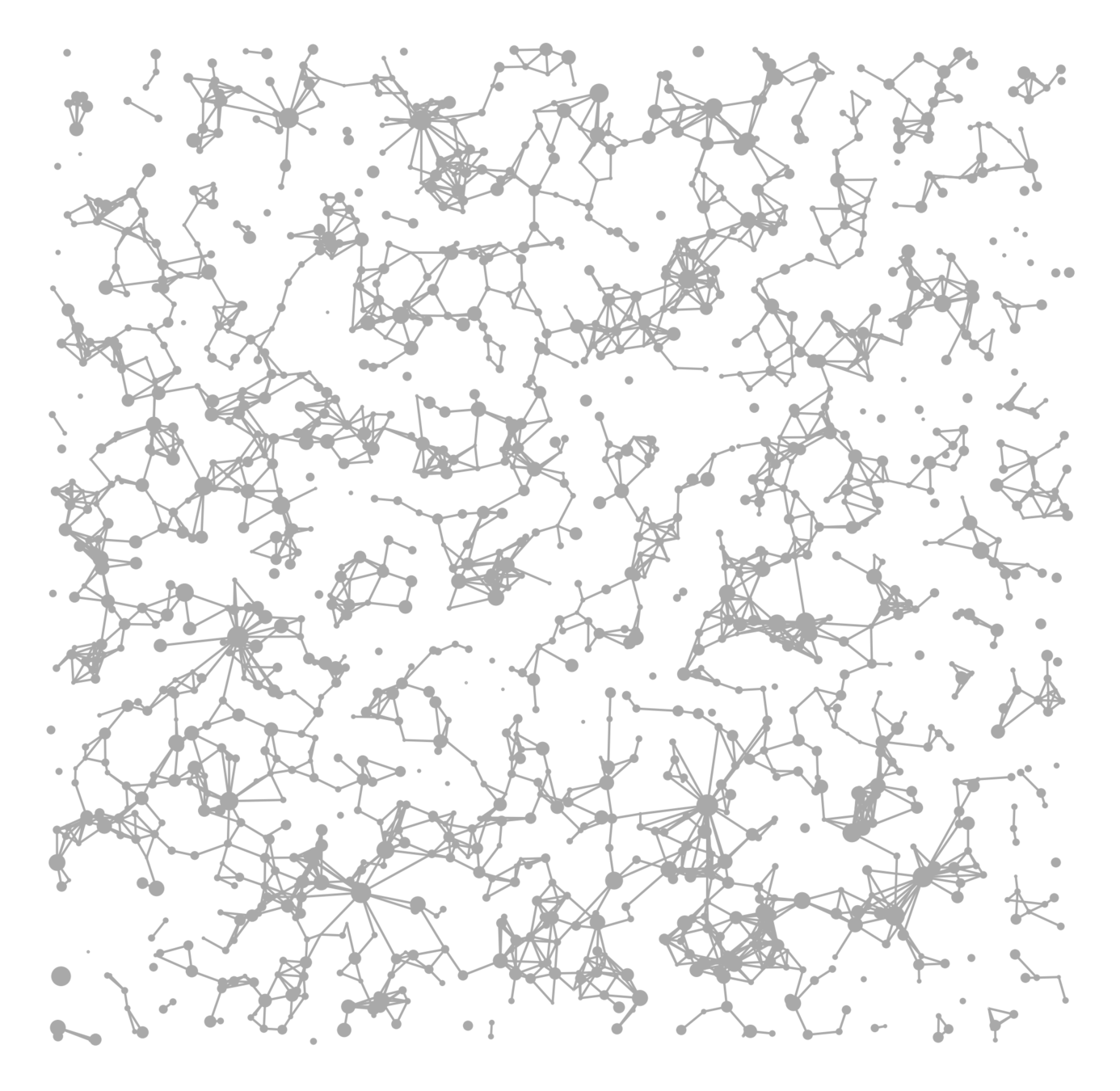
Scale-free Gilbert RG
Random geom. graph
Nearest-neighbor percolation

Long-range percolation
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
-
Spatial locations, either
- Lattice \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)
- Poisson point process (unit intensity)
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha>1\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
- Percolation \(p\in(0,1]\)
Connection probability
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=p\bigg(\frac{\beta}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\wedge 1\bigg)^\alpha$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{p}\bigg(\frac{\beta}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\wedge 1\bigg)^\alpha$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{p}\bigg(\frac{\beta}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\wedge 1\bigg)^\alpha$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{p}\bigg(\frac{\beta}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\phantom{\wedge 1}\bigg)^\alpha$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{p\bigg(}\frac{1}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\phantom{\bigg)^\alpha\wedge 1}$$
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=\phantom{p}\bigg(\frac{1}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\phantom{\wedge 1}\bigg)^\alpha$$
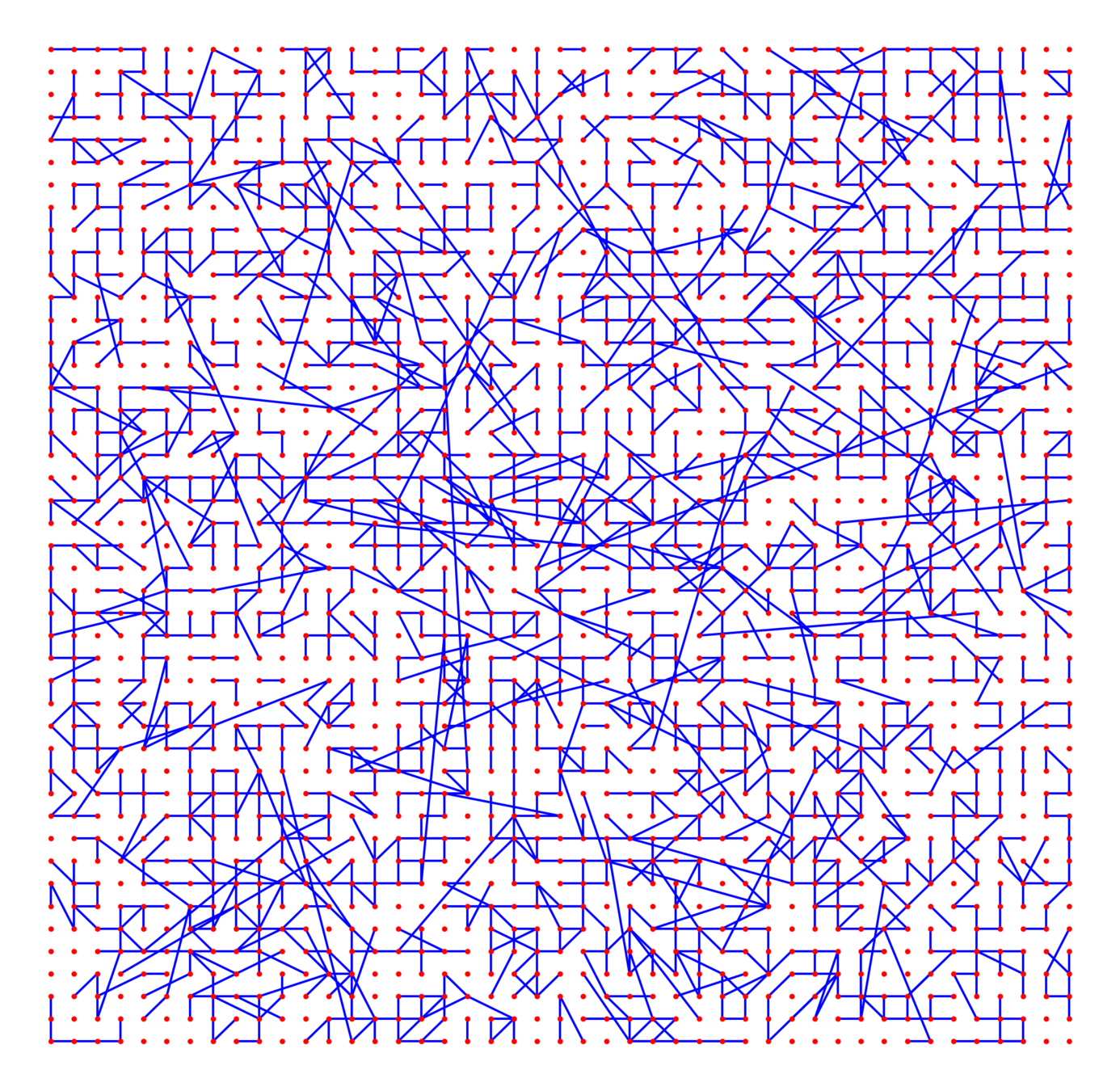
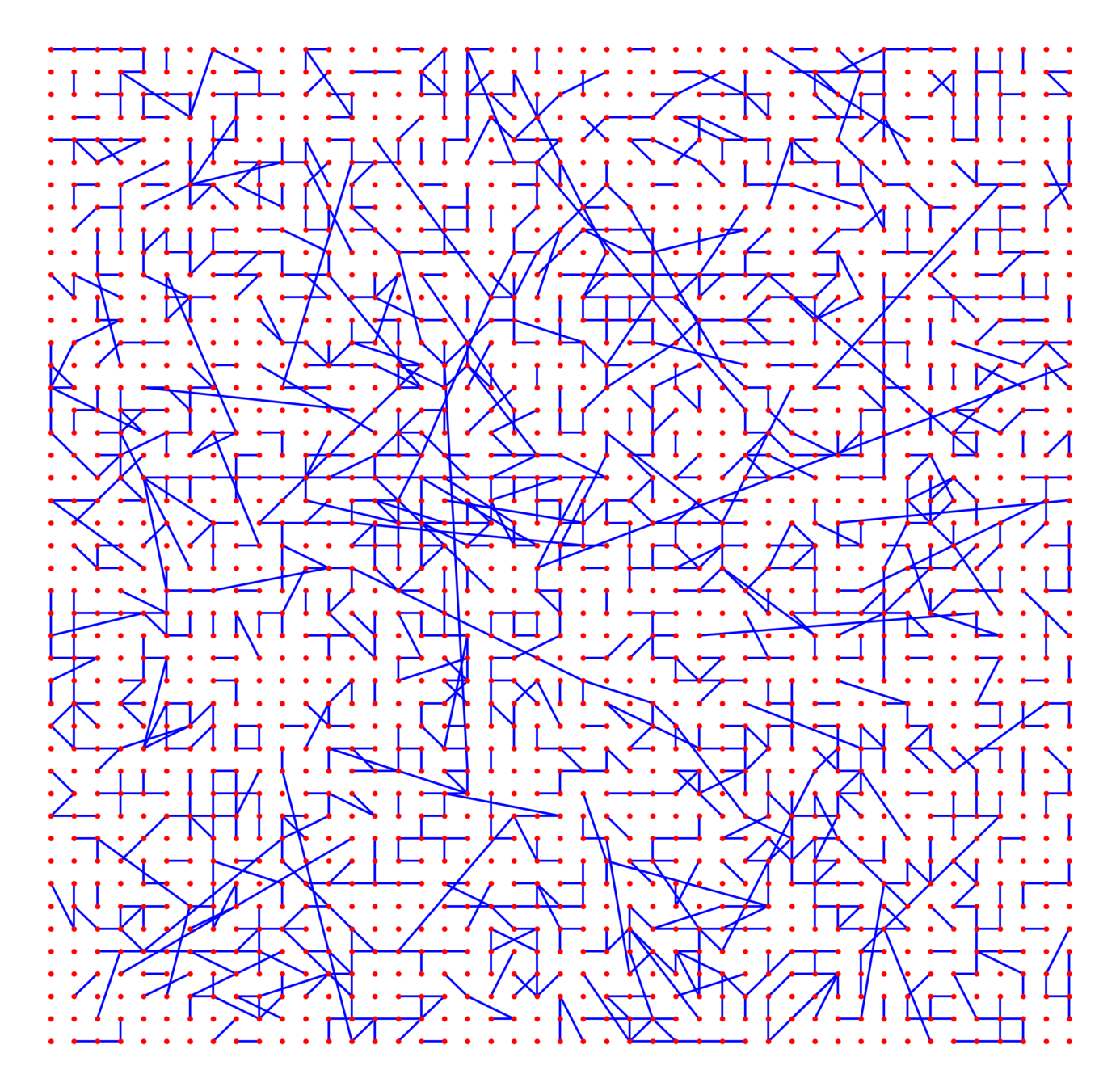
Kernel-based spatial random graphs
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
-
Spatial locations, either
- Lattice \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)
- Poisson point process (unit intensity)
- Power-law i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\):
\(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
Kernel-based spatial random graphs
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha>1\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
- Percolation \(p\in(0,1]\)
Connection probability
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=p\bigg(\frac{\beta\cdot \phantom{(w_u\cdot w_v)}}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\wedge 1\bigg)^\alpha$$
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
-
Spatial locations, either
- Lattice \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)
- Poisson point process (unit intensity)
- Power-law i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\):
\(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=p\bigg(\frac{\beta\cdot (w_u\cdot w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\wedge 1\bigg)^\alpha$$
Kernel-based spatial random graphs
Edge set \(\mathcal{E}_\infty\)
- Long-range parameter \(\alpha>1\),
- Edge-density \(\beta>0\),
- Percolation \(p\in(0,1]\)

Connection probability
Vertex set \(\mathcal{V}_\infty\)
-
Spatial locations, either
- Lattice \(\mathbb{Z}^d\)
- Poisson point process (unit intensity)
- Power-law i.i.d. weights \(w_v\ge 1\):
\(\mathbb{P}(w_v\ge w)=w^{-(\tau-1)}\),
$$\mathbb{P}\big(u\leftrightarrow v\mid \mathcal{V}_\infty\big)=p\bigg(\frac{\beta\cdot (w_u\cdot w_v)}{\|x_u-x_v\|^d}\wedge 1\bigg)^\alpha$$
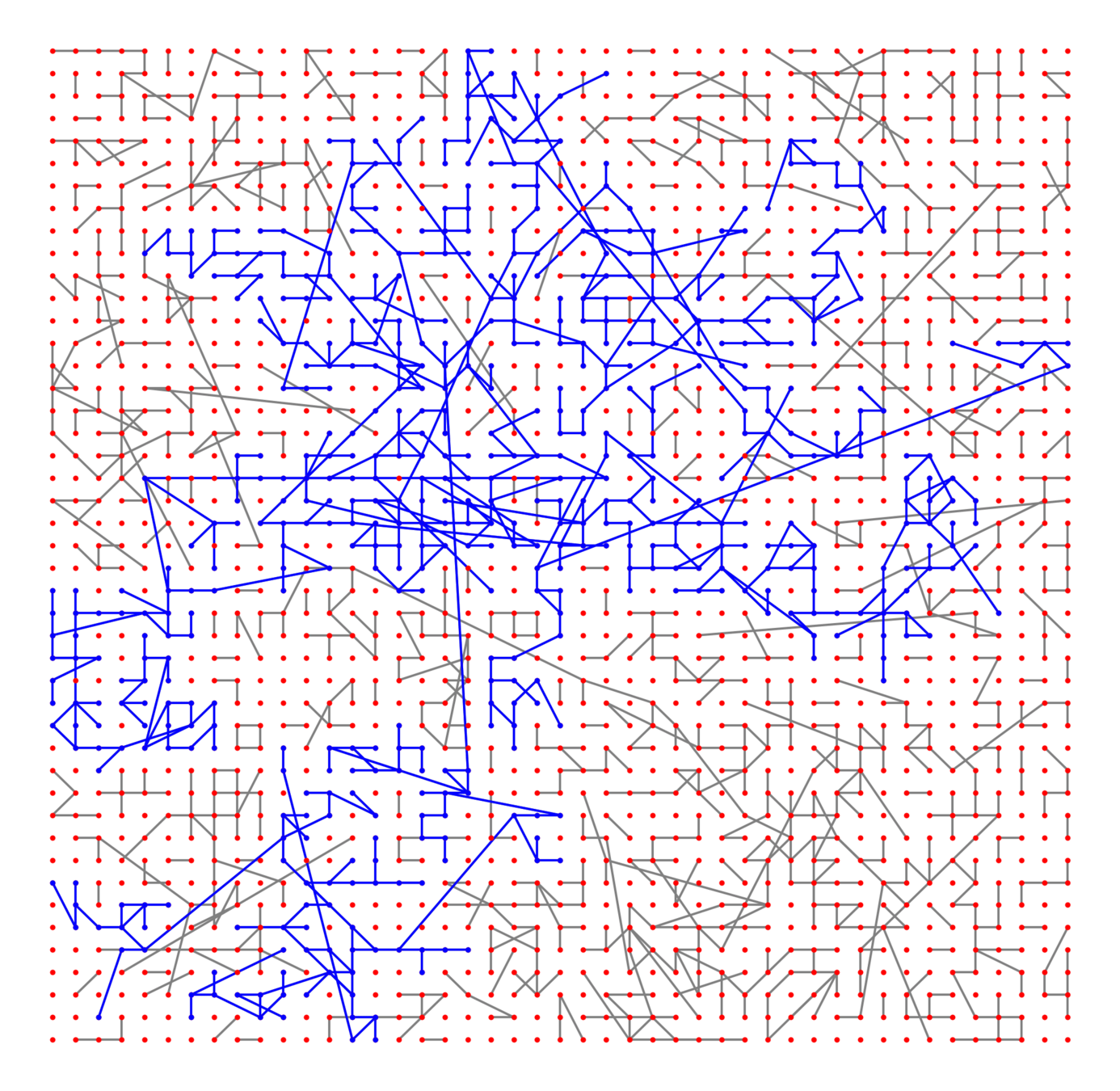
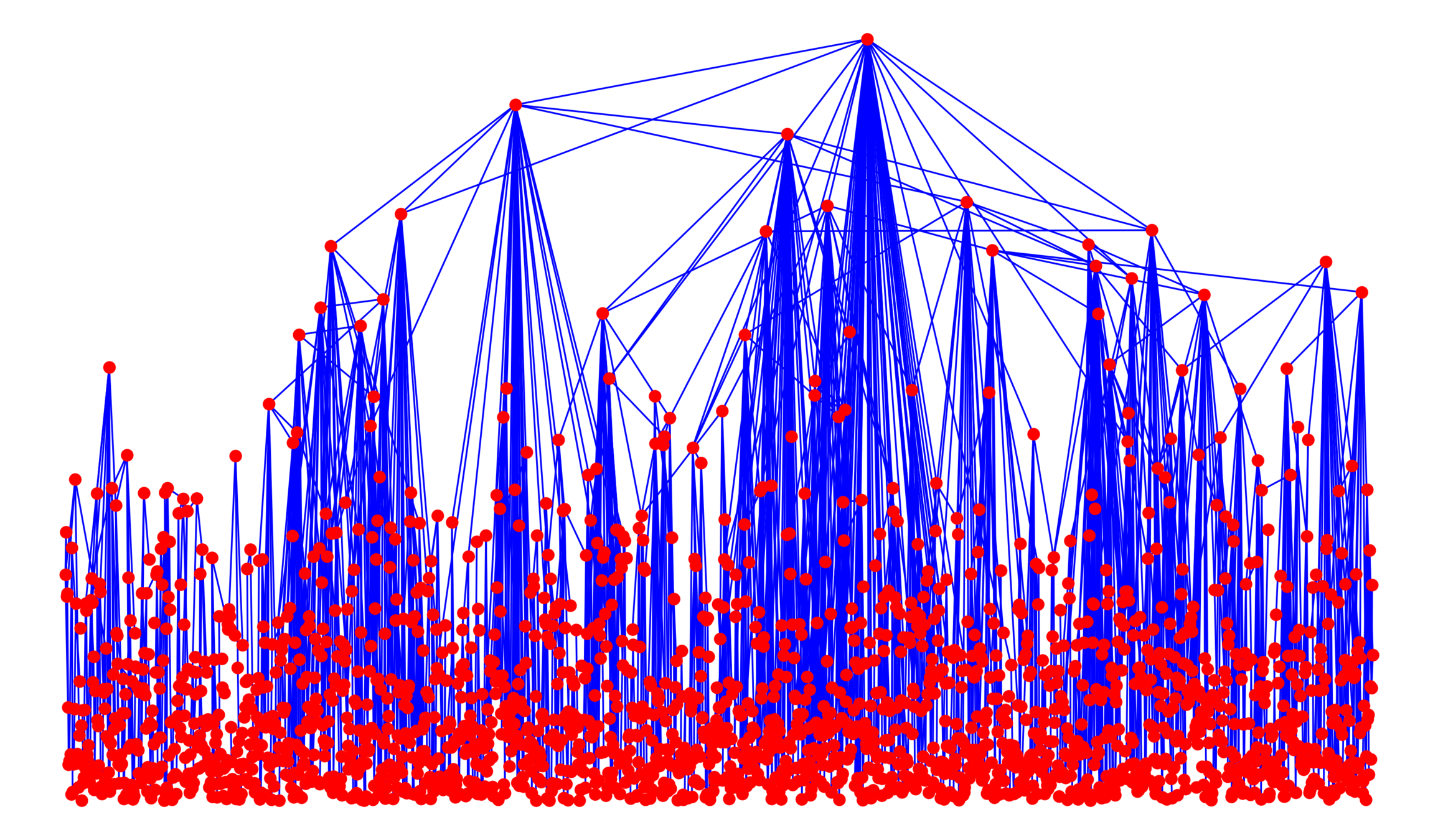
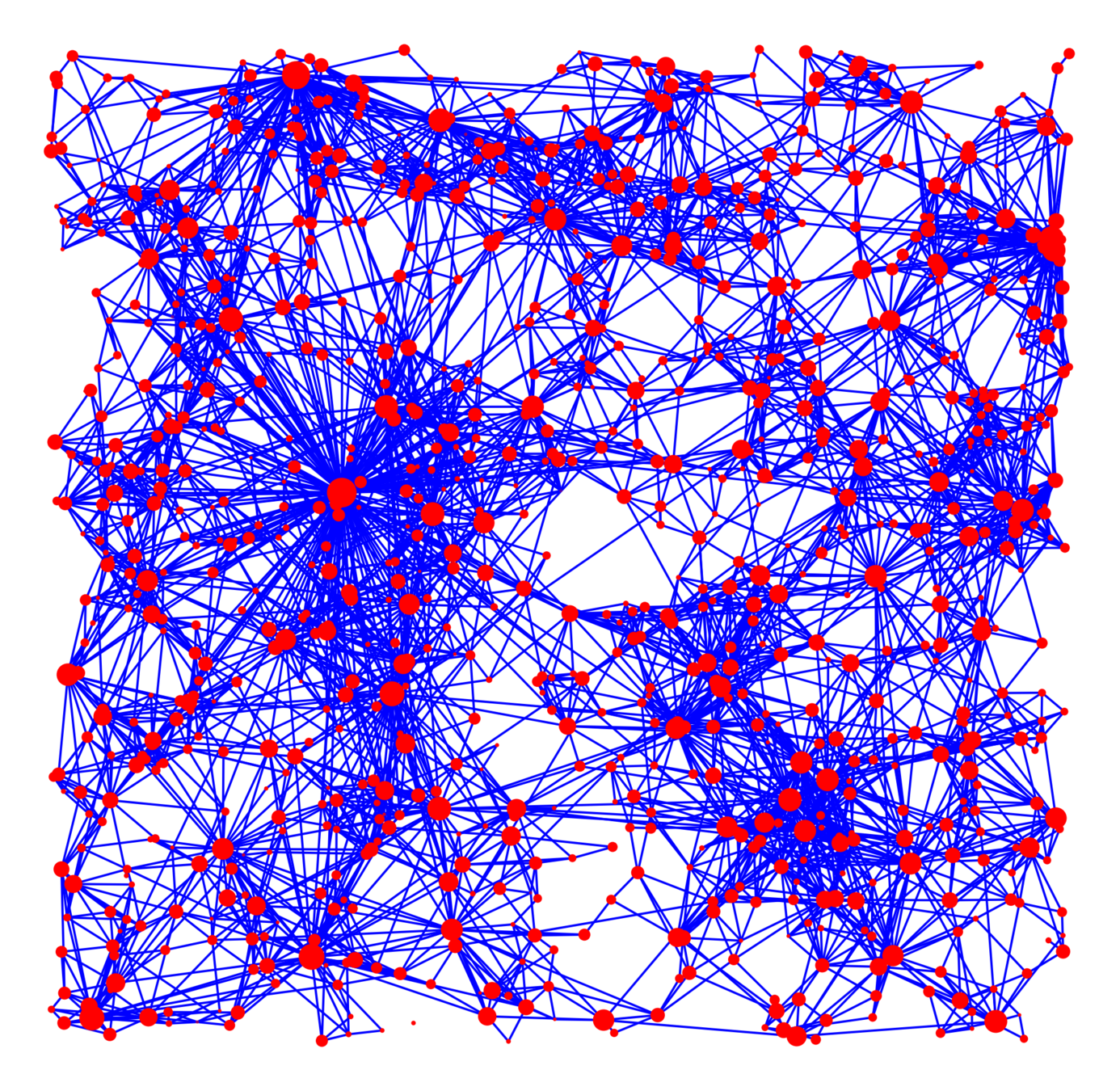
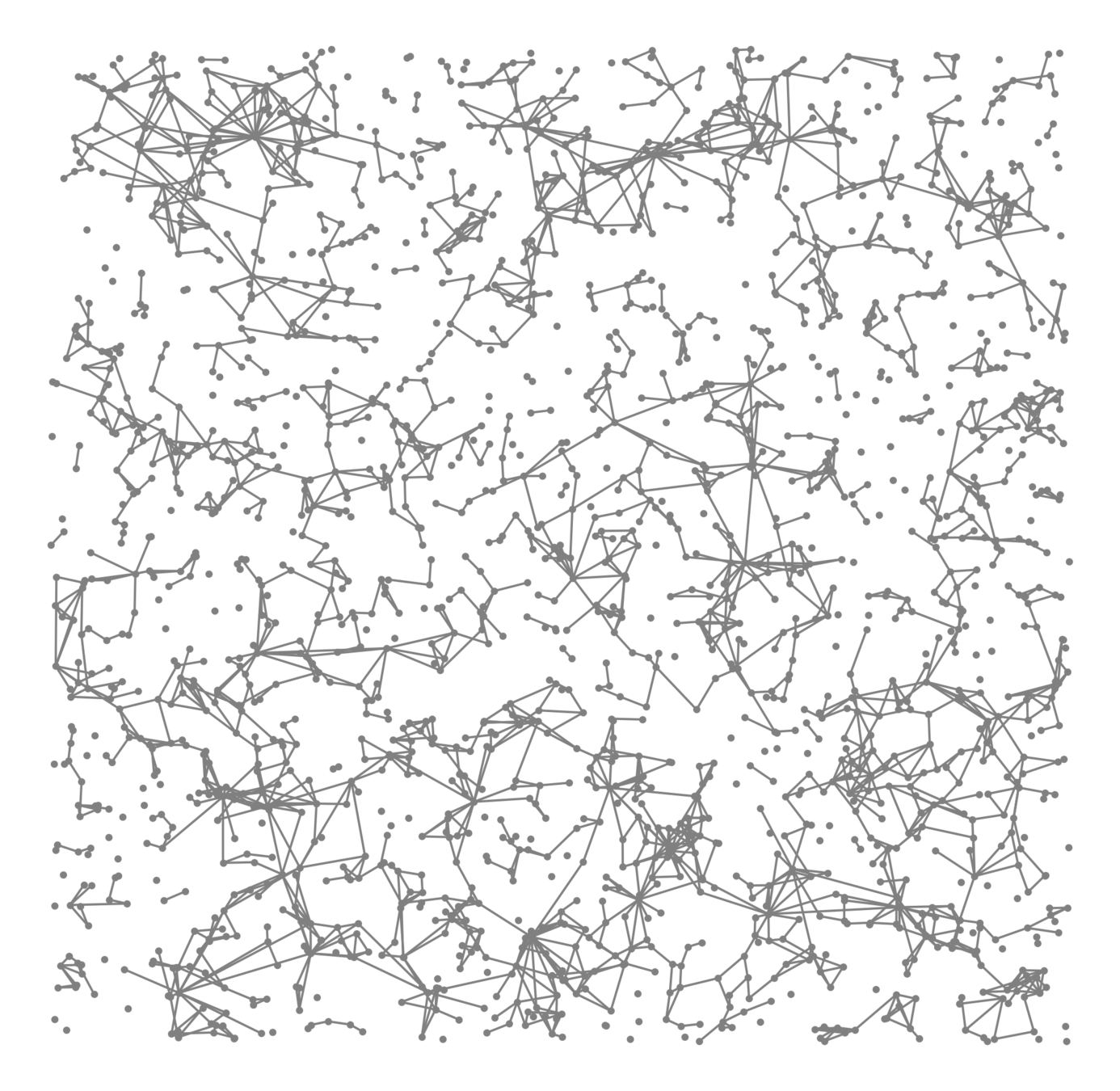
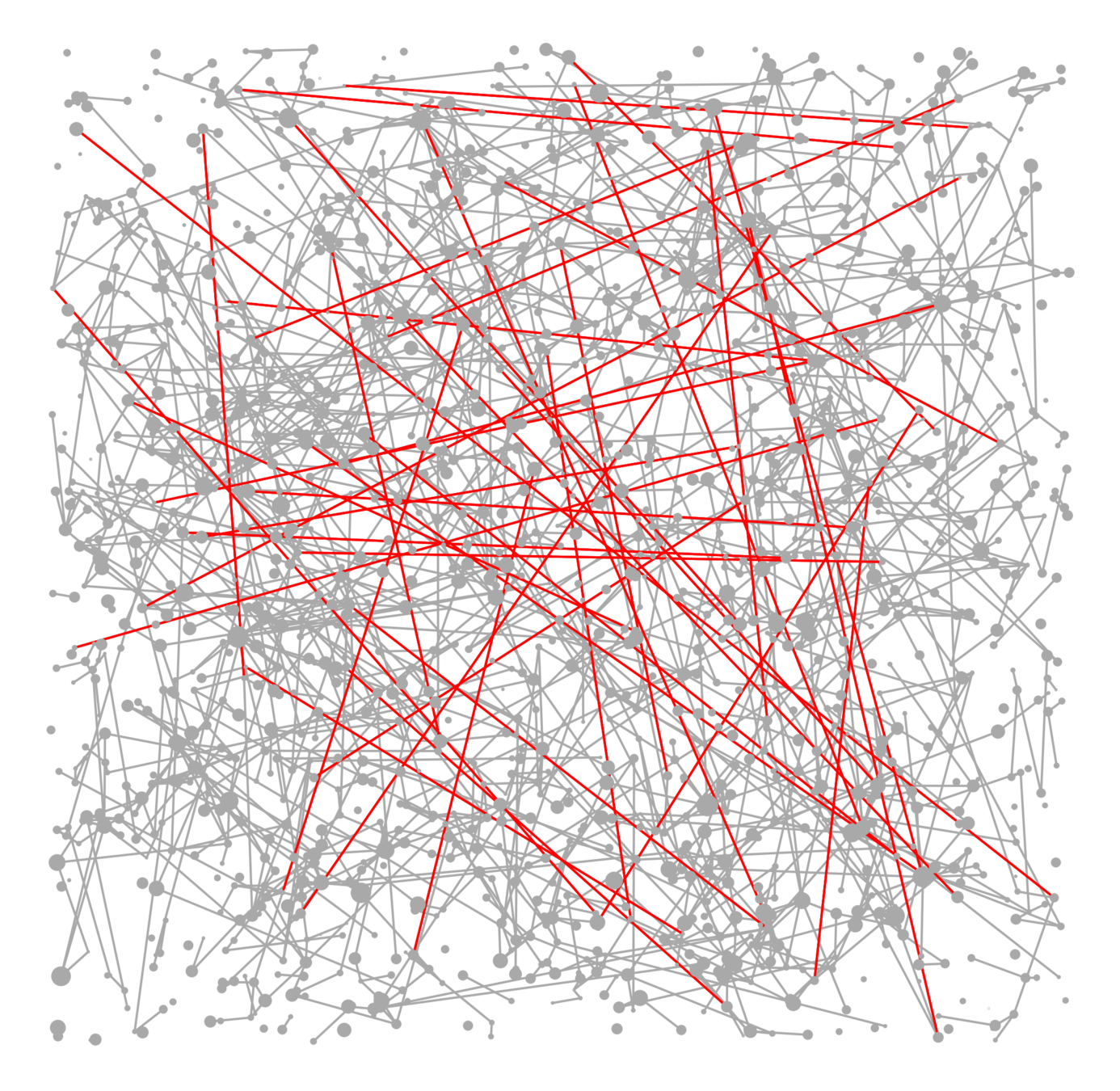
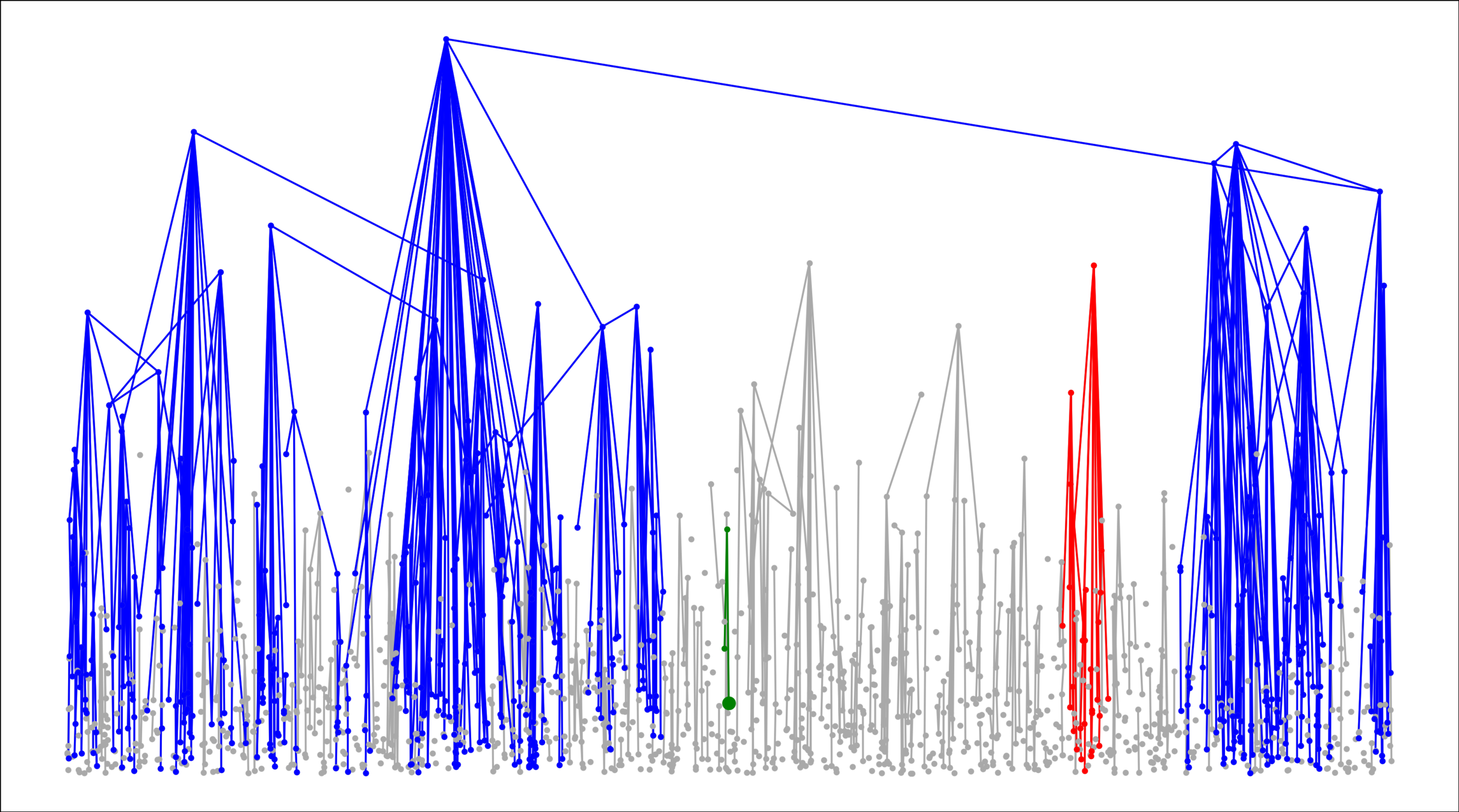
Components in supercritical graphs
-
Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Questions
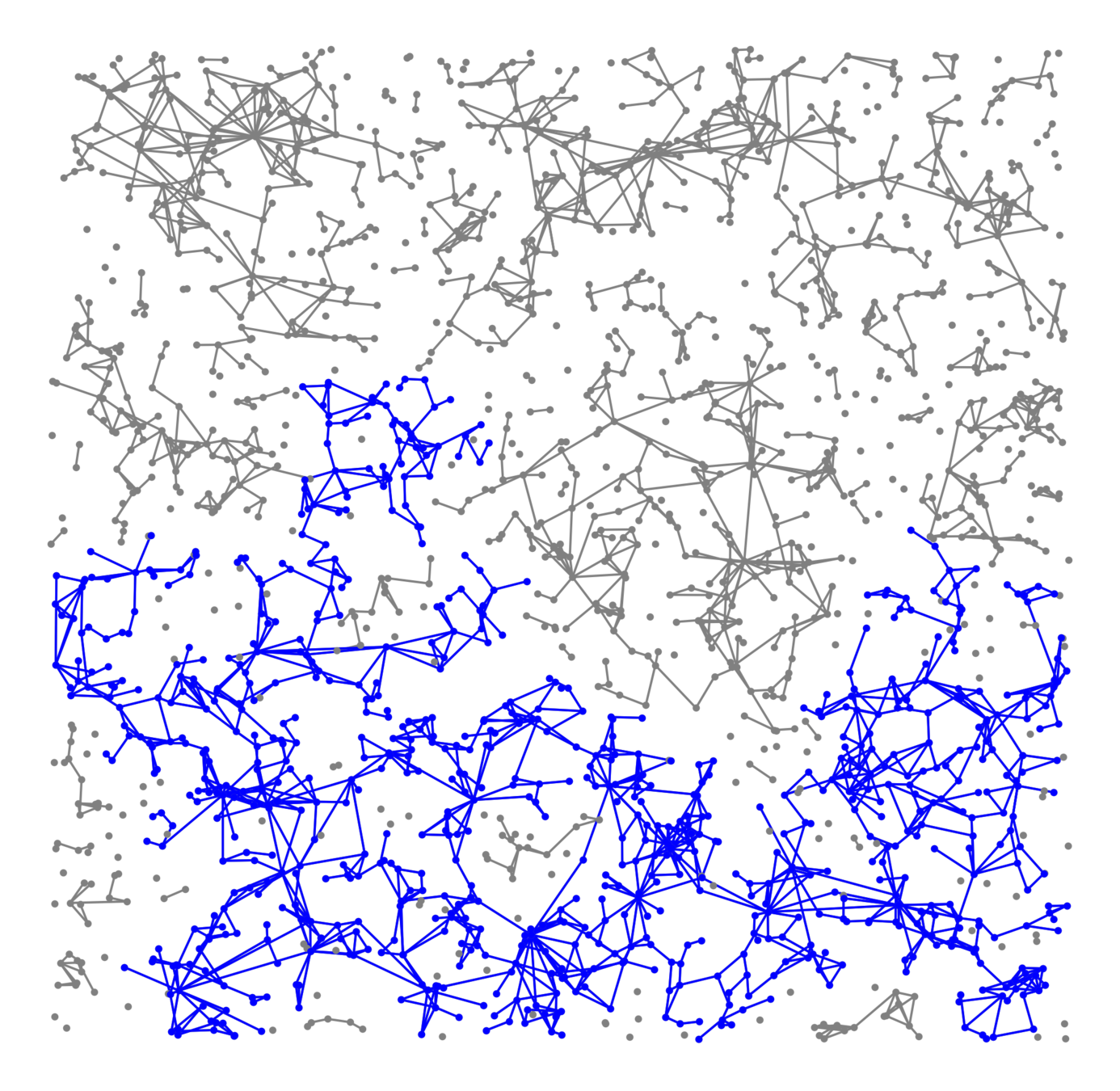




Components in supercritical graphs
-
Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Questions






Previous results
[Alexander & Chayes & Chayes '90], [Grimmett & Marstrand, '90], [Kesten & Zhang '90], ..., [Deuschel, Pisztora, '96], [Biskup '04], [Penrose '05], [Sly & Crawford'12], [Kiwi & Mitsche '17], [Lichev, Lodewijks, Mitsche, Schapira '22], [Bläsius, Friedrich, Ruff, Zeiff, '23]


Conjecture: \(\exists \zeta\in \big[\tfrac{d-1}{d},1\big)\):


Theorem. Long-range percolation (J., Komjáthy, Mitsche '24+)
Set \(\zeta_\ast := \max\{\zeta_\mathrm{long}, (d-1)/d\}\), with \(\zeta_\mathrm{long}=2-\alpha\).

If \(d=1\) and \(\zeta_\ast>0\).
If \(d\ge2\), and
\(0<\zeta_\mathrm{long}\le(d-1)/d\).
\(\zeta_\mathrm{long}>(d-1)/d\).

\(\zeta_\mathrm{long}\le(d-1)/d\), and \(p\) or \(\beta\) large.


Conjecture.
Theorem. Geom. Inhom. RG (J., Komjáthy, Mitsche '24+)
Set \(\zeta_\ast := \max\{\zeta_\mathrm{long}, (d-1)/d\}\), with \(\zeta_\mathrm{long}=\max\Big\{2-\alpha, \frac{3-\tau}{2-(\tau-1)/\alpha}\Big\}\).

If \(d=1\) and \(\zeta_\ast>0\).
If \(d\ge2\), and
\(0<\zeta_\mathrm{long}\le(d-1)/d\).
\(\zeta_\mathrm{long}>(d-1)/d\).

\(\zeta_\mathrm{long}\le(d-1)/d\), and \(p\) or \(\beta\) large.


Conjecture.
Lower bounds
Upper bounds
Lower bounds: cluster-size decay
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.





Aim: Find \(\gamma\) s.t.
Lower bounds: cluster-size decay
Aim: Find minimal \(\zeta\) s.t.




Aim: Find \(\gamma\) s.t.
Lower bounds: large deviations






(FKG)


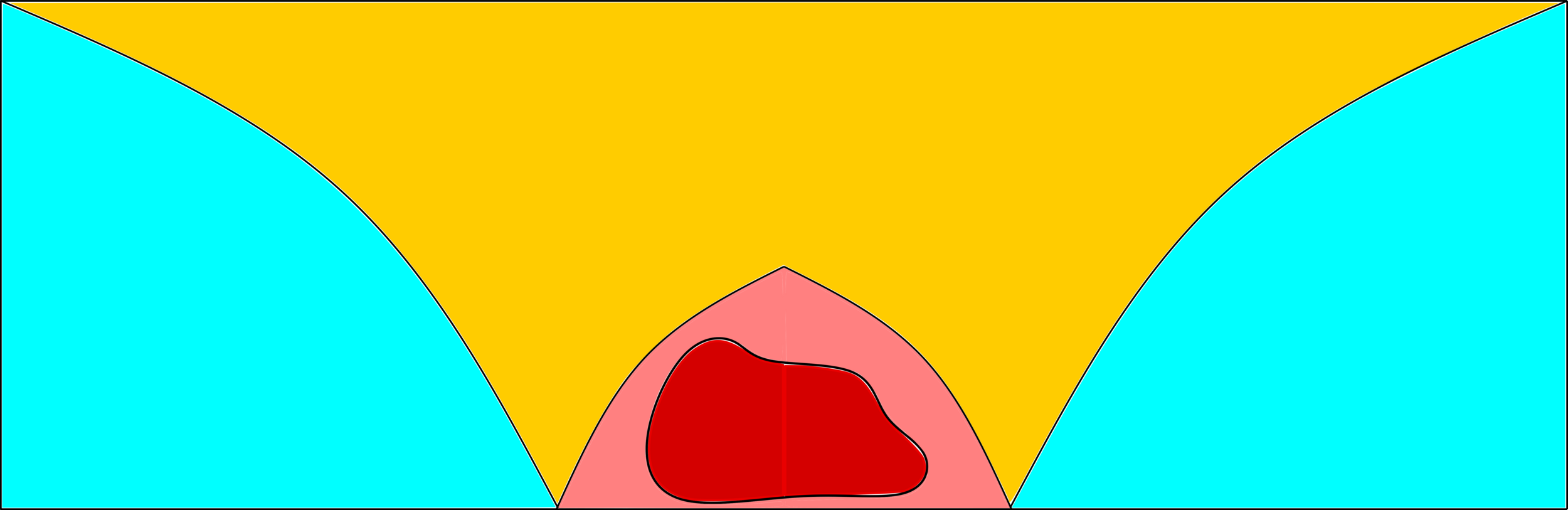



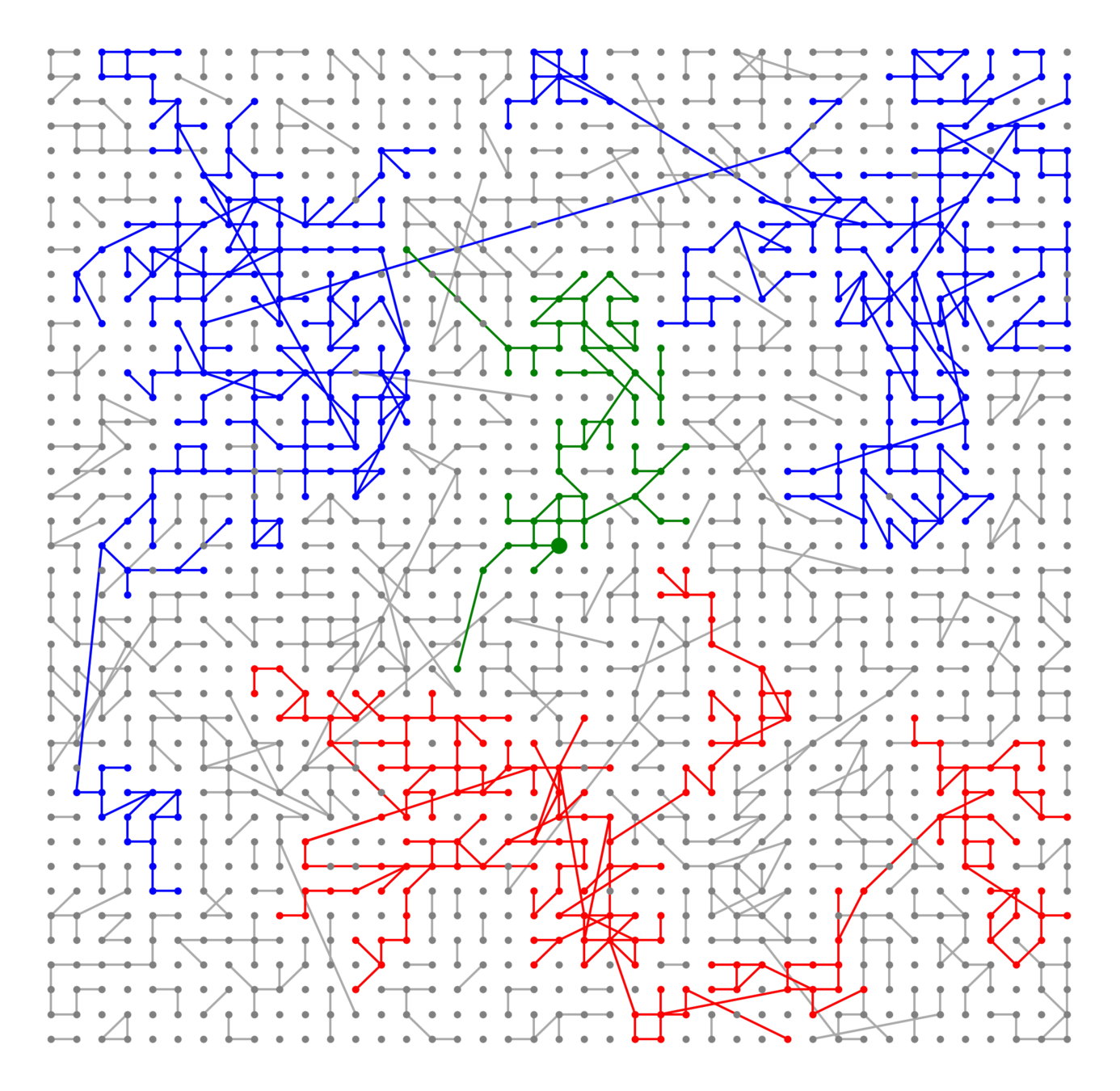
Lower bounds: \(|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|\)
\(\delta\) small
Upper bounds
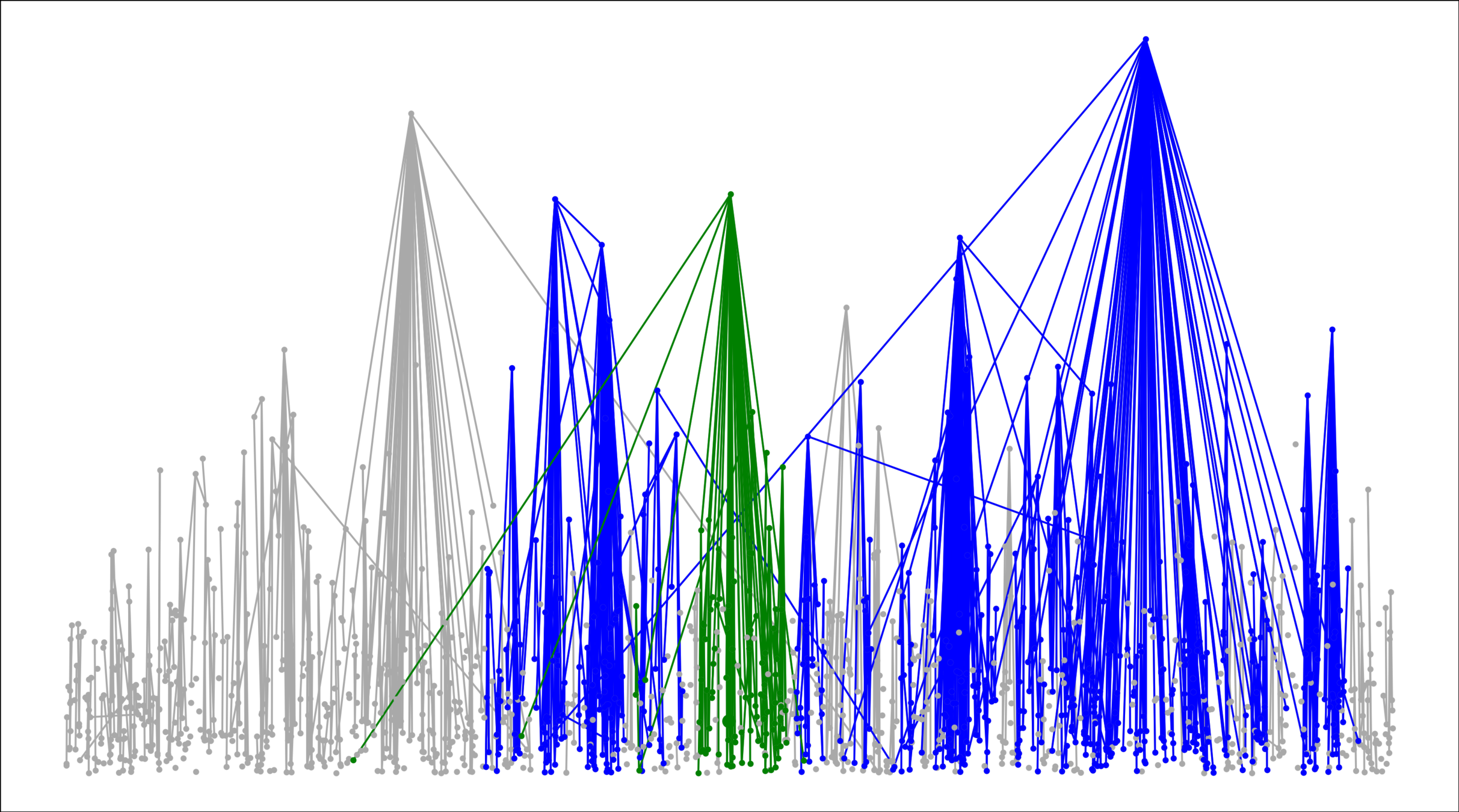
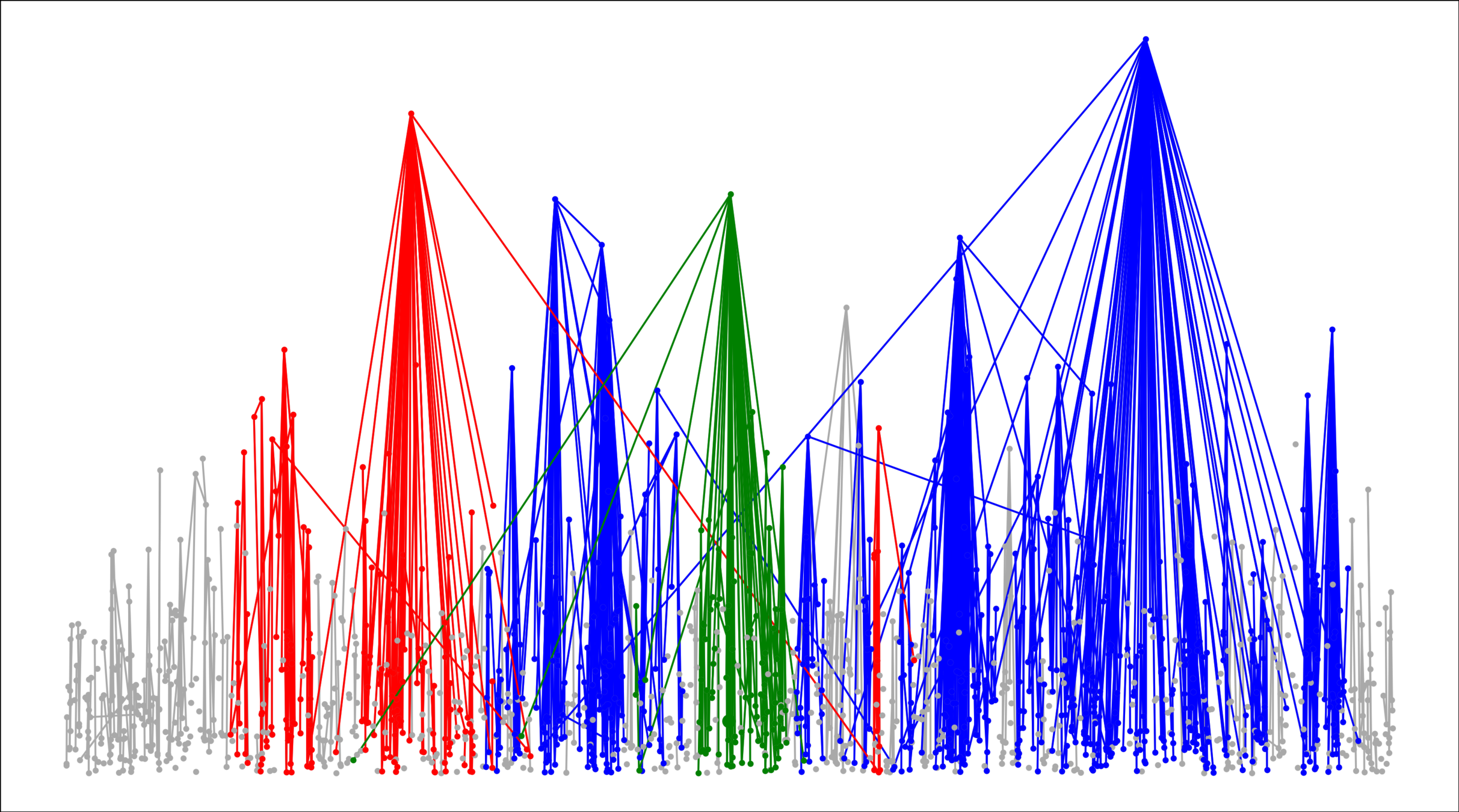
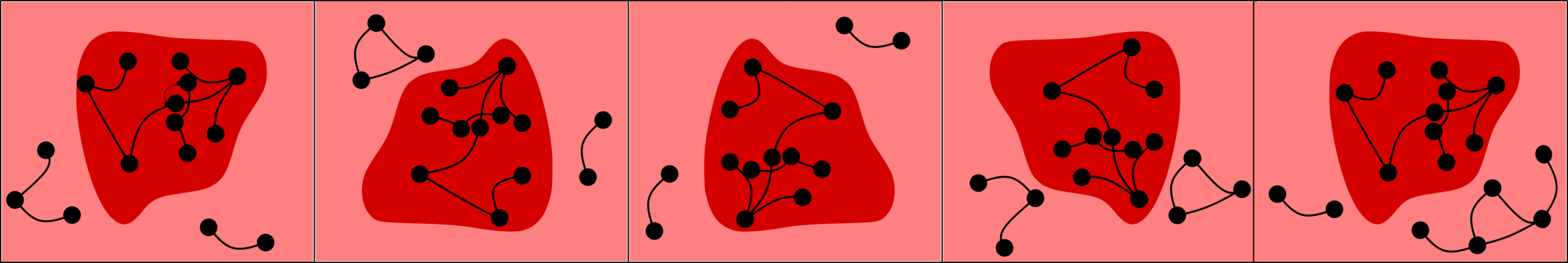
Challenge: Delocalized components
# possibilities for \(|{\color{red}2^{\mathrm{nd}}\text{-largest}}|\ge k\)

Upper bound: \(|\mathcal{C}_n^{(2)}|\)
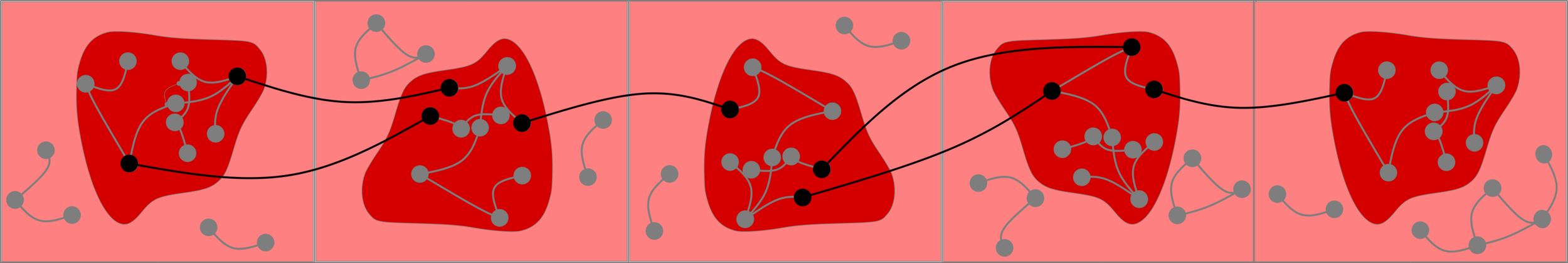
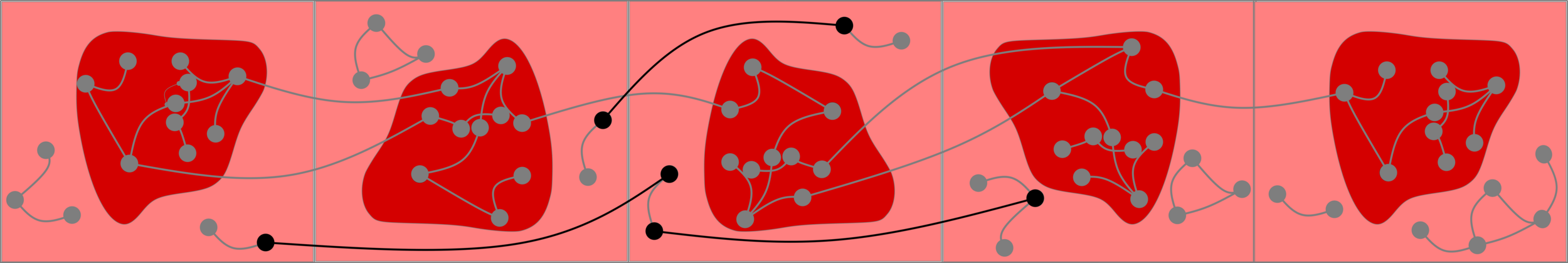

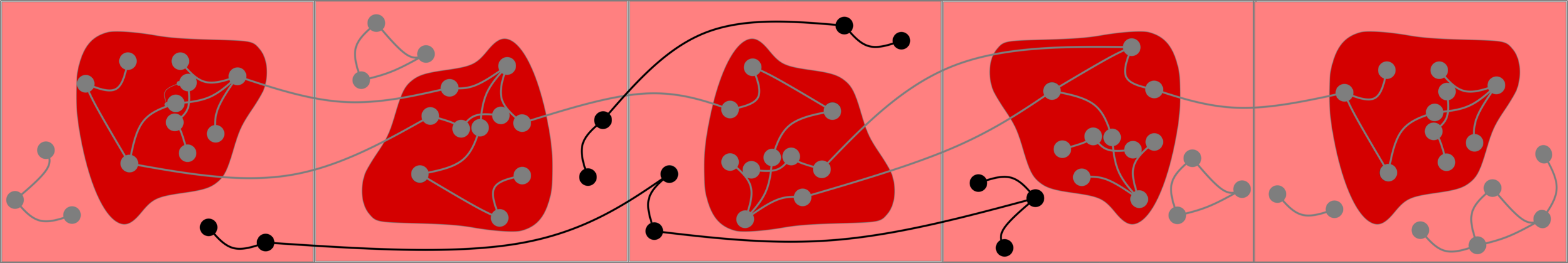
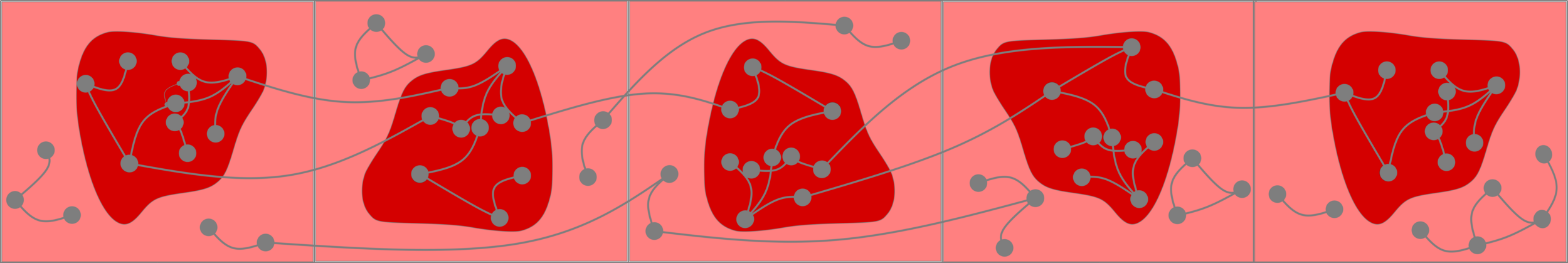
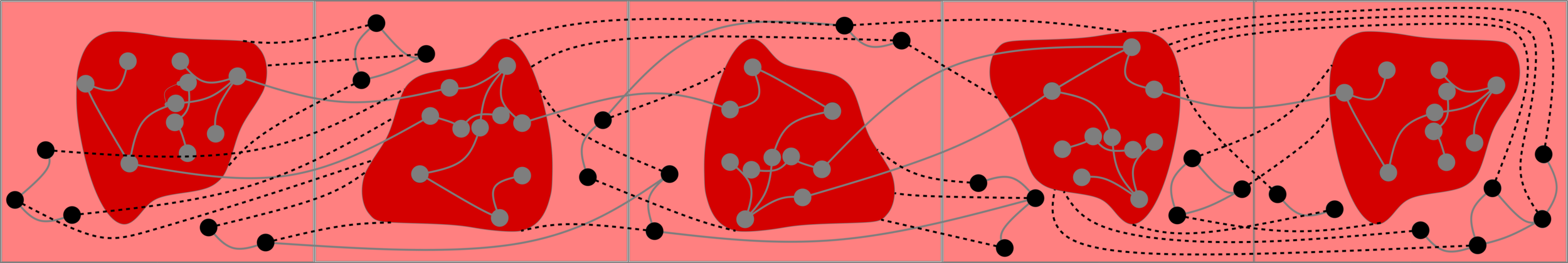
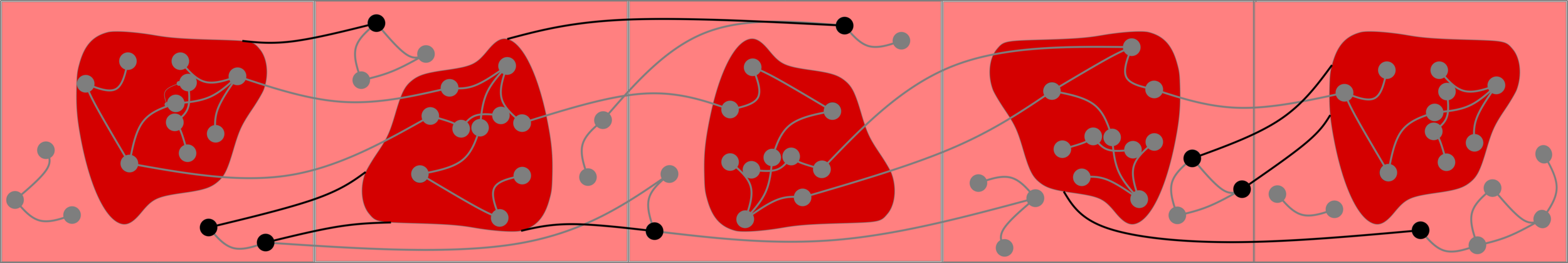
Upper bounds

Truncation
Local convergence: giant is almost local
Lower tail of large deviations
\(m_n\sim n^{2-\alpha}\) boxes
Lower tail of large deviations

\(m_n\sim n^{2-\alpha}\) boxes
Upper bounds

What about other value \(\zeta_\ast\)?

Description of weight distribution in large components
Prevent "small-to-large" merging
Components in supercritical graphs
- Largest component \({\color{blue}\mathcal{C}_n^{(1)}}\):
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Lower tail large deviations
- Upper tail large deviations
Answered questions (\(d=1\))




Tales on tails: large deviations
Lower tail:
Upper tail:
# hubs (\(w_v\sim n\)) required: increase density from \(\vartheta\) to \(\vartheta+\varepsilon\)


(Second-)largest component in supercritical spatial random graphs
- Cluster-size decay
- Second-largest component
Open problems:
-
Largest component:
- Linear in box size
- Law of large numbers
- Large deviations
Answered questions (\(d=1\))
- Phase transition boundaries.
- Partial results \(d\ge 2\)
- Extension from PPP to grid
- Central limit theorem





- \(\zeta\in\big[(d-1)/d, 1\big)\)
Thank you!

Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Small
Large
Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Lower bounds
Upper bounds

Remarks.
- \(\zeta_\ast<0\): subcritical*
-
\(d\ge 2\):
- \((d-1)/d\)
- partial results: upper bounds
- Product kernel: 2nd term
Power-law degrees: \(\tau>2\)
\(d\ge 2\)
* [Gracar, Lüchtrath, Mönch '22]
Theorem. (J., Komjáthy, Mitsche '23+)
Set
If \(\zeta_\ast>0\), then LLN for \(|{\color{blue}\text{largest}}|\), and
Long-range parameter: \(\alpha>1\)
Example 2:
Geom. Inhomog. RG in \(d=1\)
Copy of (Second-)largest component in spatial inhomogeneous random graphs
By joostjor
Copy of (Second-)largest component in spatial inhomogeneous random graphs
- 340



